My original target purpose is very simple, build deploy several webserver and assigned a external ip for internet to access it.
Most kubernetes newbie install guide won’t mention how to do that. actually that’s very simple, for external ip, it needs a load balance controller like metallb for create a external ip address to access web server. and an Ingress contoller like Traefik for http/https route to right pods .

Above is a figure to describe relationship about metallb/traefik and kubernetes.
Please reference previous article (Install Kubernetes on ARM64 Ubuntu 18.04)about how to setup environment.
Install Helm
First, install Helm, helm is a kubernetes packages manager. it can help to install traefik, for some package, like traefik, it’s not easy to install manually, I tried, but fail. Use helm to install is a good idea.
Following instruction can download and install helm, or you can visit helm webpage for latest version
Following is command to download and install helm.
wget https://get.helm.sh/helm-v2.15.1-linux-arm64.tar.gz tar xvf helm-v2.15.1-linux-arm64.tar.gz sudo mv linux-arm64/helm /usr/bin
Default helm(tiller seems doesn’t support ARM64 archeticture, so, it needs to use third party binary code for tiller. In here we used tiller-multiarch.
helm init --tiller-image=jessestuart/tiller
Helm install error message
When you run helm install command, if see error message like below, please try to follow this step to solve it. (ref: TILLER AND ROLE-BASED ACCESS CONTROL and forbidden: User “system:serviceaccount:kube-system:default” cannot get namespaces in the namespace “default)
Create a rbac-config.yaml like following text
(ref. User “system:serviceaccount:kube-system:default” cannot get namespaces in the namespace “default” )
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: tiller
namespace: default
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: tiller
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: tiller
namespace: defaultRun following command to create and upgrade helm initial
kubectl create -f rbac-config.yaml helm init --service-account tiller --history-max 200 --tiller-image=jessestuart/tiller --upgrade
or run those commands directly.
kubectl create serviceaccount --namespace kube-system tiller
kubectl create clusterrolebinding tiller-cluster-rule --clusterrole=cluster-admin --serviceaccount=kube-system:tiller
kubectl patch deploy --namespace kube-system tiller-deploy -p '{"spec":{"template":{"spec":{"serviceAccount":"tiller"}}}}'
helm init --upgrade --service-account tiller
Install metallb
Automatically Install
It can use helm to install automatically, first create a metallb-config.yaml, contain like below.
configInline:
address-pools:
- name: default
protocol: layer2
addresses:
- 192.168.110.80-192.168.110.100
Save it, and run follow command to apply it.
helm install --name=metallb --namespace=metallb-system -f metallb-config.yaml stable/metallb
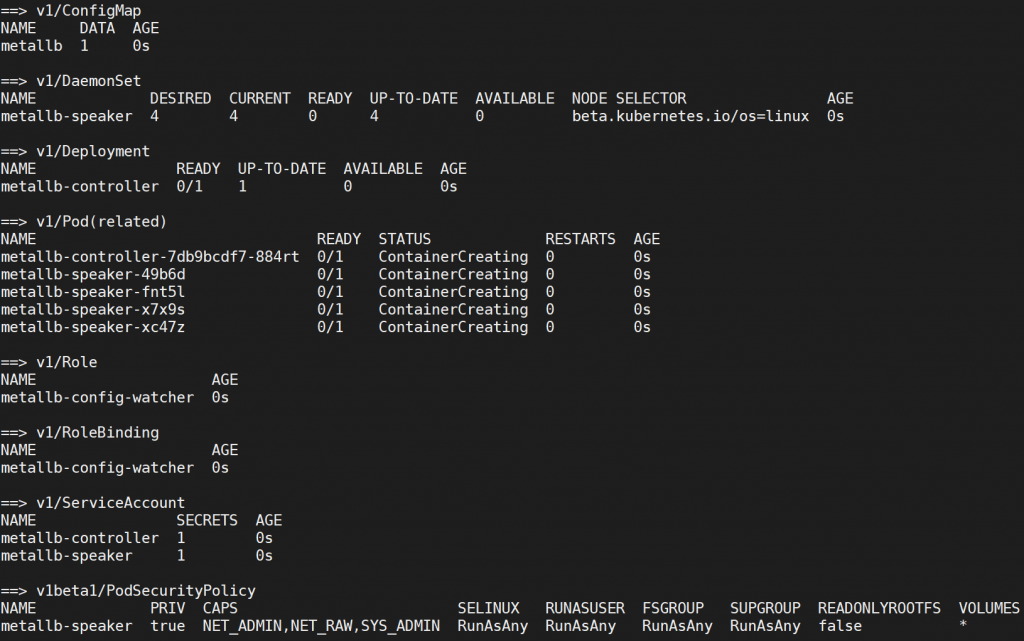
Manually Install
It also can install metallb manually, run following command to install it.
It will install v0.8.1, it can visit metallb website to check latest version.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/google/metallb/v0.8.1/manifests/metallb.yaml
Add a new file name metallb.yaml and put follow text
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
namespace: metallb-system
name: config
data:
config: |
address-pools:
- name: my-ip-space
protocol: layer2
addresses:
- 192.168.110.70/28
Apply it
kubectl apply -f metallb.yaml
Install Traefik
Traefik is an open-source Edge Router that makes publishing your services a fun and easy experience.
Following is command to initial helm and used helm to initial traefik.
helm install stable/traefik --name traefik --set dashboard.enabled=true,serviceType=NodePort,dashboard.domain=dashboard-traefik.techarea.org,rbac.enabled=true --namespace kube-system
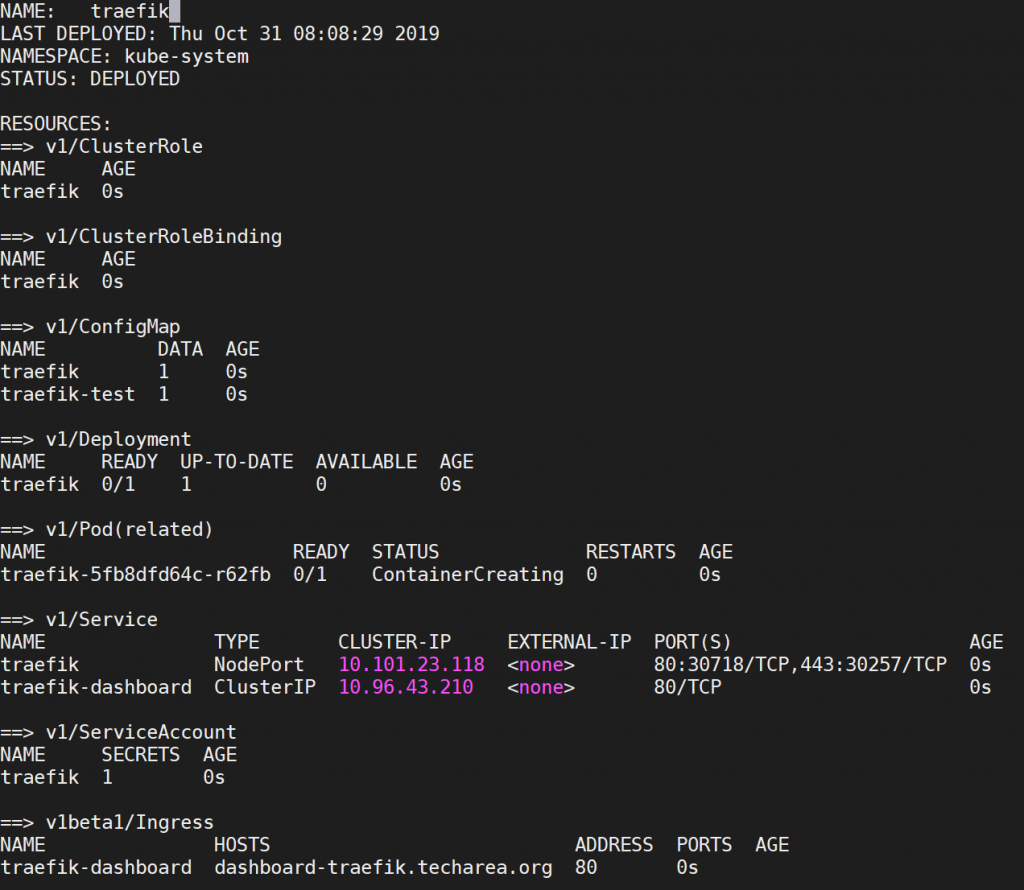
Traefik Dashboard
When used helm to install traefik, it also install traefik dashboard on dashboard-traefik.techarea.org.
Used following command to get traefik web service ip
kubectl describe svc traefik --namespace kube-system
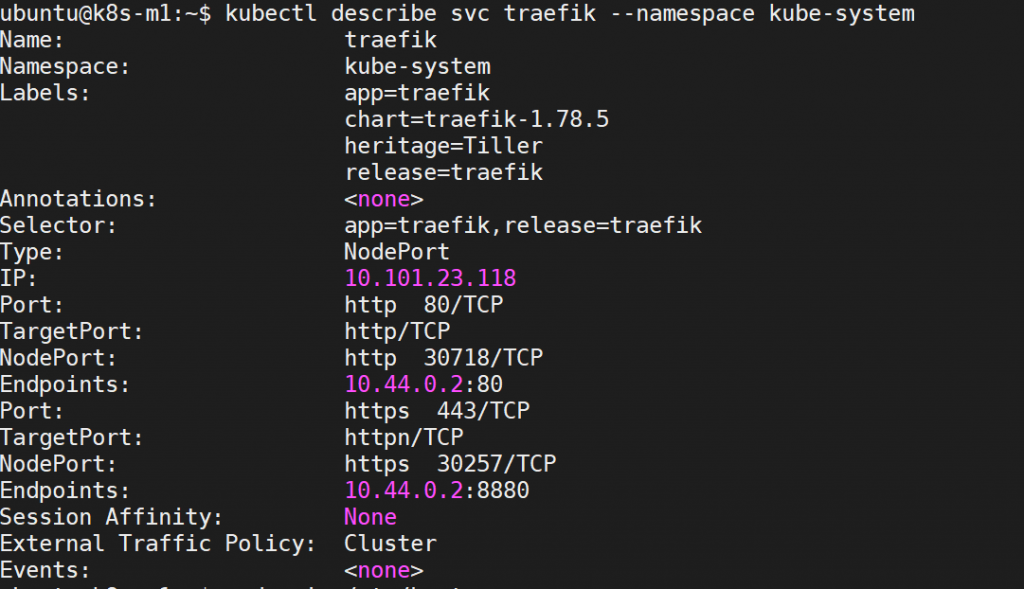
It can see a http hosted on 10.44.0.2 , add 10.44.0.2 daskboard-traefik.techarea.org to browser PC’s hosts file, it can use browser to access traefik dashboard .
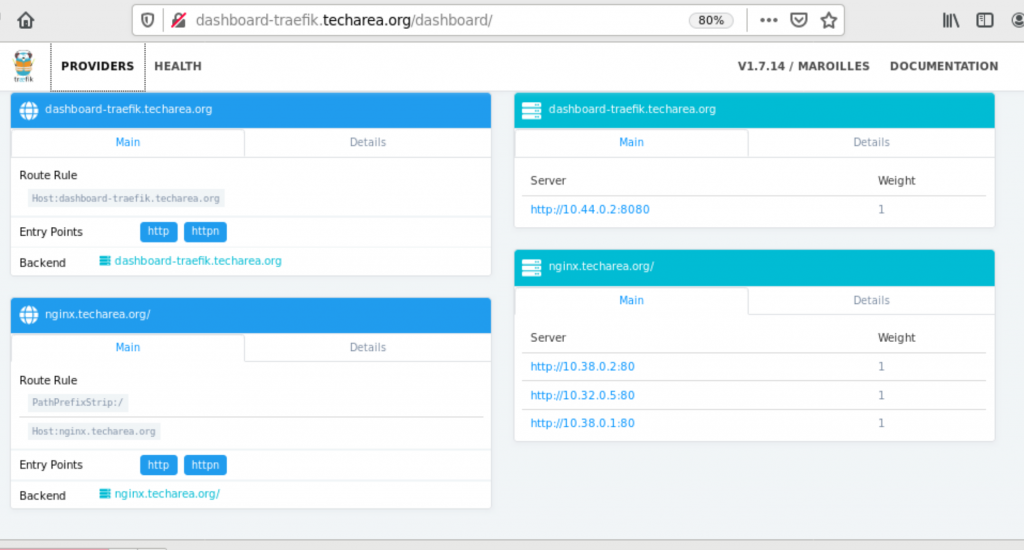
Create a nginx web site
In here, we create three nginx website, and assigned a external ip address, it will also assign a domain name, traefik will have load balance traffic to all three pods.
First create a new file called nginx.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 4
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: nginx
type: LoadBalancer
---
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: traefik
traefik.ingress.kubernetes.io/rule-type: "PathPrefixStrip"
name: nginx
spec:
rules:
- host: nginx.techarea.org
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: nginx
servicePort: 80
replicas means how many pods you went to create, in here, we used 3, it will create 3 pods on clients.
host means url, in here is nginx.techarea.org.
used kubectl to apply it.
kubectl apply -f nginx.yaml
Get current service status

We can see external ip is 192.168.110.80, add 192.168.110.80 nginx.techarea.org to your browser PC’s host file, and used browser to access nginx.techarea.org, it can see welcome nginx.
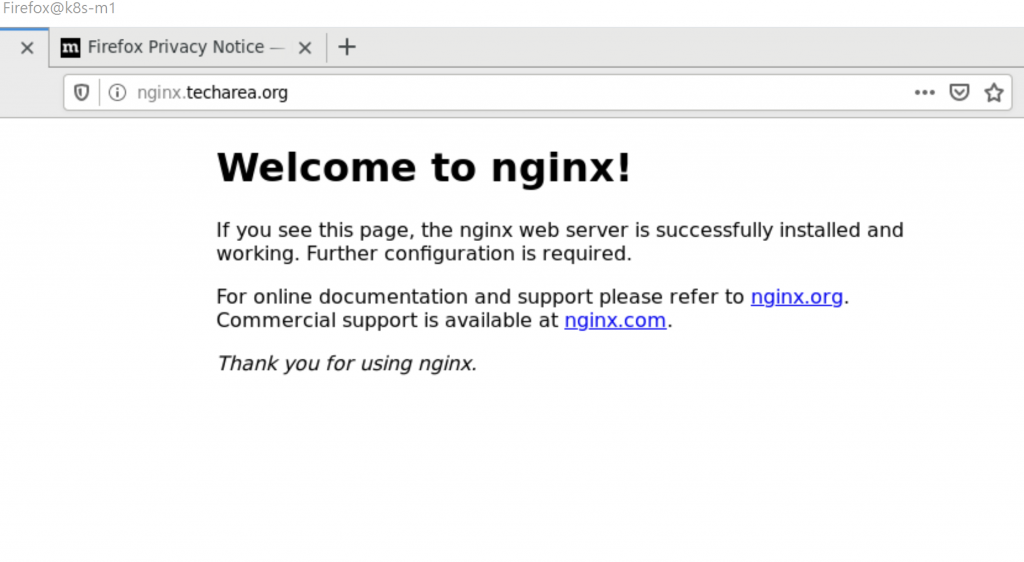
Test Load Balance
Now we finished install traefik and metallb successfully, next step is to verified does that really work ?
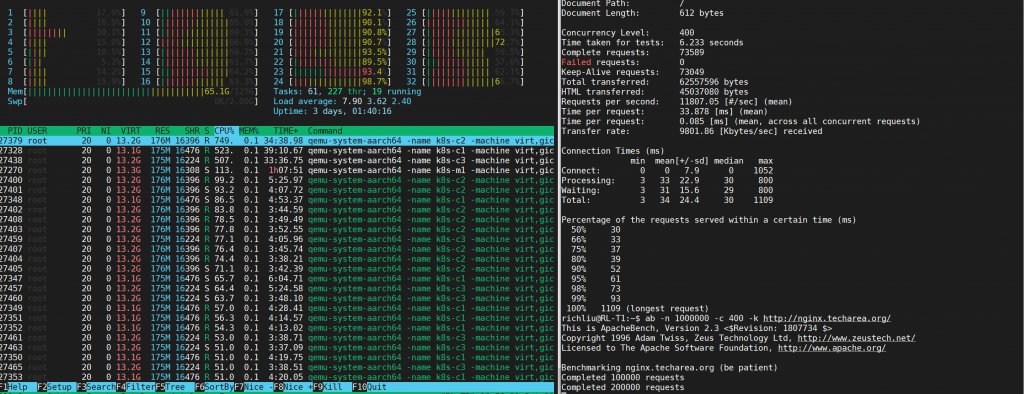
it can use another host to run ab (apache benchmark to do this test) and used htop observe CPU loading.
Following is example to test nginx, if don’t see all CPU has loading, try to increase pods instance, like 4 .
ab -n 1000000 -c 400 -k http://nginx.techarea.org/
Below is example result for nginx load balance.
See, that’s easy job, right ?




發佈留言