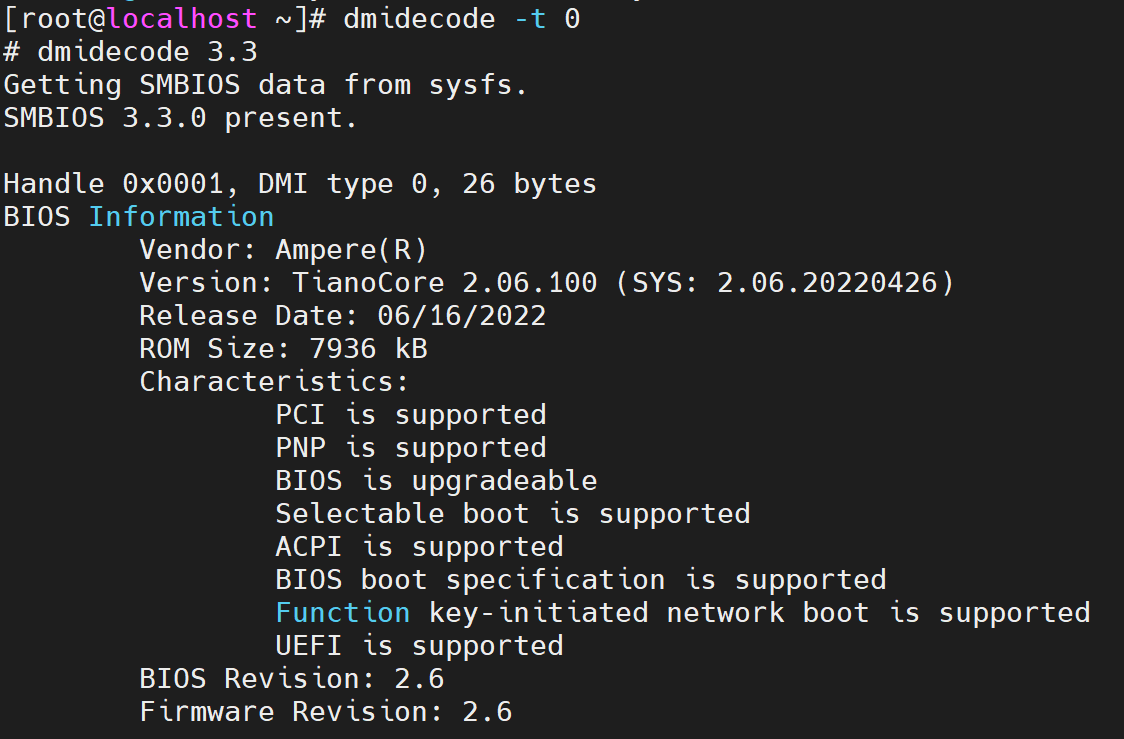
Ampere announce Altra CPU, it’s a 80 cores ARM64v8 CPU for cloud native workloads. Altra Max CPU is 128 cores. Follow the CPU, Ampere also has a CRB (customer reference board) named Mt. Jade, and Ampere also open source OpenBMC and EDKII source code for Mt. Jade platform.
This article is personal note, all information can be found from internet. And open source project keeps going, it might be some minor differences when you find this article.
Table of Contents
Before Build Source Code
This procedure runs on ARM64 platform, it should be also run on x86 platform, but I have not try it.
Build environment : Ampere eMAG CPU (32 cores) with 256G DRAM and uses 64G/128G RAM to build code, sometime if it cannot finsih compile tasks, probably your DRAM is not sufficient to build the code, I tried 16G and it doesn;t work.
Because host is running Ubuntu 22.04, and OpenBMC and EDKII only can be built on Ubuntu 18.04, so, it needs to use either virtual machine or contianer technologies to have Ubuntu 18.04 environment.
This note uses qemu to prepare build environment, tried docker but it doesn’t work, probably I will re-try it someday.
If use NFS or qemu overlayers filesystem to bridge folders ourside into VM, it might cause build problem, so, please increase disk size for you virtual machine virtual disk size, use nfs or share folder for copy images or source code only.
If want to build a workable EDKII code and run it on Ampere Mt. Jade platform, it needs to have Ampere fimware ATF and SCP binary, it might register Ampere customer connect to download those image files, without it, it only can build OpenBMC binary.
Prepare Build Environment
Get the Ubuntu 18.04 cloud image
$ wget https://cloud-images.ubuntu.com/releases/bionic/release/ubuntu-18.04-server-cloudimg-arm64.img $ sudo apt install qemu-efi
Prepare hostname and userdata for VM
it needs to prepare two files, meta-file and user-data, following is example for meta-file
instance-id: Image-openbmc local-hostname: openbmc
user-data file, this example username is ubuntu, password is ubuntu
#cloud-config
password: ubuntu
chpasswd: { expire: False }
ssh_pwauth: True
ssh_authorized_keys:
- ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQC+Y/6m4XFeEGKqR2H7wbsUQUVWvB0gC/+CeJqfyvOX++SETKapFtI5CiidkyW/B1GQM4XUlmE9zPlCAcolPfMpXB0CNQQ5l0F5Z+FW6b4RVjFV/KEcQ7R3XkKRa0XhC6hKkNc5P95fNhXr8Do1bSEmd9mPIiOrFaUEZ9EReO+ZTsGsytFIuQV8rOZfQjClktXrqk3F6jJ+TV3THcVNpKvnLfps56Hc/j9jdiadLv91yuifz4lCMbv/D/0hMtf4KhN5tV//QRgUxEUeC7aPW6sKD2GMYMxc9UsSyRRQ9IFWjJMkgzKyuxgNKe7u4WjERFoxEUrmFK01UsrX+lRw9e9n user@hostname
Than, it can create a configure file for QEMU
$ cloud-localds -v cloudinit.img user-data meta-file
Increase Ubuntu cloud image disk size, bigger is better, suggest more than 200G, minimal should be around 100G.
$ qemu-img resize ubuntu-18.04-server-cloudimg-arm64.img +200G
Prepare UEFI BIOS and storage for booting
dd if=/dev/zero of=flash0.img bs=1M count=64 dd if=/usr/share/qemu-efi/QEMU_EFI.fd of=flash0.img conv=notrunc dd if=/dev/zero of=flash1.img bs=1M count=64
Running the VM script, it will also create a QEMU virtfs for file sharing, but do not use that folder to build code. How to access share folder, it can reference this article QEMU Share Directory with Host Without Networking
IMAGE1=ubuntu-18.04-server-cloudimg-arm64.img
sudo qemu-system-aarch64 -name vm1 \
-machine virt,gic_version=3,accel=kvm,usb=off \
-cpu host -m 128G \
-smp 32,sockets=1,cores=32,threads=1 \
-nographic -nodefaults \
-pflash flash0.img -pflash flash1.img \
-drive file=$IMAGE1,if=none,id=disk1 \
-device virtio-blk-device,drive=disk1 \
-drive file=cloudinit.img,if=virtio,format=raw \
-virtfs local,path=/nvme/obmc,mount_tag=host0,security_model=passthrough,id=host0 \
-netdev tap,id=net0,ifname=tap0 \
-device virtio-net-device,netdev=net0,mac=52:54:00:11:11:12 \
-serial telnet::9001,server,nowait > guest_log-1.txt 2>> guest_log-1.txt
Build Mt. Jade EDKII
Prepare VM environment
After login into VM, it needs to install software to compile EDKII.
Command to install basic packages.
sudo apt update sudo apt install -y git vim tmux lftp net-tools ethtool bc sudo apt install -y \ build-essential uuid-dev acpica-tools nasm \ python3 python3-distutils python3-pip \ gawk sudo apt install -y libssl-dev gnu-efi sudo apt install bison flex sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python3 1
Next step is follow this document to download Ampere EDKII source code and setup enviroment.
https://github.com/AmpereComputing/edk2.git
First, prepare build environment parameters, if VM reboot, it needs to re-run it.
export WORKSPACE=/nvme/tianocore
mkdir -p $WORKSPACE
cd $WORKSPACEexport PACKAGES_PATH=$PWD/edk2:$PWD/edk2-platforms
# PACKAGES_PATH is default include path, sometimes miss package can include more directories here.
# if still cannot find some files, try to run submodules command on next step again.
export PACKAGES_PATH=$PWD/edk2:$PWD/edk2-platforms:$PWD/edk2-non-osi/:$PWD/edk2-platforms/Features/
Chang into that folder, clone Ampere Computiner edk2 source code.
cd $WORKSPACE git clone https://github.com/AmpereComputing/edk2.git cd edk2 git submodule init && git submodule update cd .. git clone https://github.com/AmpereComputing/edk2-platforms.git
Get build environment
This step is to build the basic tools.
cd $WORKSPACE . edk2/edksetup.sh # Build BaseTool, only need to run once make -C edk2/BaseTools
After compiled the EDK2 basic tool, next step is to prepare edk2-platforms and edk2-ampere-tools
edk2-ampere-tools has a very good build script,
it can help to build the EDK2 and also package ATF into together.
we will introduct it on following steps.
cd edk2-platforms git checkout -b test remotes/origin/ampere # make a link to library to fix some problem ln -sf /nvme/tianocore/edk2-platforms/Features/Intel/OutOfBandManagement . cd .. git clone https://github.com/AmpereComputing/edk2-ampere-tools
Build and Sign the image
Because current tree Atftool migrate to OpenSSL 3.0, and Ubuntu 18.04 still use OpenSSL 1.0x,
I choice to roll back to old version to support OpenSSL 1.0x, support it can build Atftool on Ubuntu 22.04 or compile OpenSSL 3.0 manually, I might try it later.
cd /nvme/tianocore mkdir -p AtfTools cd AtfTools git init git remote add origin -f https://github.com/ARM-software/arm-trusted-firmware.git git config core.sparseCheckout true echo -ne "include/tools_share\nmake_helpers\ntools/cert_create\ntools/fiptool" > .git/info/sparse-checkout git -C . checkout --track origin/master # Due to current AtfTool only support OpenSSL 3.0 , switch to previous version git checkout -b test b94bf967e62b23a376a5026de69d06a0e8d6bf78 make -C tools/cert_create CRTTOOL=cert_create $ make -C tools/fiptool FIPTOOL=fiptool
configure PATH to fiptool and cert_create
cd /nvme/tianocore export PATH=$PATH:$PWD/AtfTools/tools/cert_create:$PWD/AtfTools/tools/fiptool
This step is parepare Mt. Jade ATF and SCP binary for compile, it needs to get both binary file from Ampere customer connect. and also suggest to use the same version as OpenBMC/EDKII
cd $WORKSPACE mv <path to>/altra_atf_signed_2.06.20220426.slim . mv <path to>/altra_scp_signed_2.06.20220426.slim . cd edk2-ampere-tools ./edk2-build.sh -b RELEASE Jade --atf-image $WORKSPACE/altra_atf_signed_2.06.20220426.slim --scp-image $WORKSPACE/altra_scp_signed_2.06.20220426.slim
If everything is perfect, the binary code would be looks like below.
Results: /nvme/tianocore/edk2-ampere-tools/BUILDS/jade_tianocore_atf_2.06.100
total 45888
-rw------- 1 root root 3343 Jun 15 12:40 dbukey.auth
-rw------- 1 root root 2002 Jun 15 12:40 del_dbukey.auth
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2008 Jun 15 12:38 jade_board_setting.bin
-rw-rw-r-- 1 ubuntu ubuntu 14532 Jun 15 04:08 jade_board_setting.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 670845 Jun 15 12:40 jade_scp_2.06.100.cap
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 262144 Jun 15 12:40 jade_scp_2.06.100.dbu.sig.img
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 8126464 Jun 15 12:38 jade_tianocore_2.06.100.fd
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 14040229 Jun 15 12:40 jade_tianocore_atf_2.06.100.cap
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 13631488 Jun 15 12:40 jade_tianocore_atf_2.06.100.dbu.sig.img
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 10225352 Jun 15 12:38 jade_tianocore_atf_2.06.100.img
------------------------------------------------------------
Ampere Jade (AARCH64) RELEASE pass
------------------------------------------------------------
pass 1
fail 0
It can use the jade_tianocore_atf_2.06.100.img for firmware update.
Note: When latest time I compile the edkII binary, latest version will fail to build, it need to roll back to previous version.
Manual Build EDKII
If still want to build EDKII manually, here is some command can help you.
cd edk2-platform build -a AARCH64 -t GCC5 -b RELEASE -D SECURE_BOOT_ENABLE -p Platform/Ampere/JadePkg/Jade.dsc or to use all CPU to compile the EDKII. build -n `nproc` -a AARCH64 -t GCC5 -b RELEASE -D SECURE_BOOT_ENABLE -p Platform/Ampere/JadePkg/Jade.dsc
the generated image on $WORKSPACE/Build/Jade/RELEASE_GCC5/FV/BL33_JADE_UEFI.fd,
for this case, on the /nvme/tianocore/Build/Jade/RELEASE_GCC5/FV/BL33_JADE_UEFI.fd
then, it needs to use ampere special tool to generate EDKII image with Ampere ATF image.
Build Mt. Jade OpenBMC
Prepare build environment
Before build OpenBMC, it needs to install necessary packages,
it can build both OpenBMC and EDKII on the same VM, or it can build it on different VM.
Following is necessary packages for OpenBMC.
$ sudo apt-get install -yy \
build-essential \
chrpath \
cpio \
debianutils \
diffstat \
gawk \
git \
iputils-ping \
libdata-dumper-simple-perl \
liblz4-tool \
libsdl1.2-dev \
libthread-queue-any-perl \
locales \
python \
python3 \
socat \
subversion \
texinfo \
wget \
zstd
Download Open BMC source code and OpenBMC build script.
$ cd /nvme $ git clone https://github.com/ampere-openbmc/openbmc.git $ git clone https://github.com/openbmc/openbmc-build-scripts.git
modify openbmc-build-scripts/build-setup.sh around line #140,
replace “Clone in openbmc master to ${obmc_dir}” to https://github.com/ampere-openbmc/openbmc.git
it can download right source code.
git clone ${branch} https://github.com/ampere-openbmc/openbmc.git
If you use more than 32 cores to build the source code, it might cause compile fail because some compile tool might have problem on build code on ARM64 massive code. A easy way to check that is run dmesg to check whether Linux kernel has OOM killer on some package compile fail message like nodejs.
Limited CPU number to 32 , modify openbmc-build-scripts/build-setup.sh, on line 84.
84 # num_cpu=${num_cpu:-$(nproc)}
85 num_cpu=32
Build OpenBMC
This step is to prepare test build environment
$ cd /nvme $ target=mtjade WORKSPACE=/nvme/openbmc branch="--branch ampere --single-branch" ./openbmc-build-scripts/build-setup.sh
Setup openbmc machine type to mt. Jade and compile OpenBMC.
$export TEMPLATECONF=meta-ampere/meta-jade$ export TEMPLATECONF=meta-ampere/meta-jade/conf/templates/default/ $ export TMPDIR=/nvme/temp $ export LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8 $ cd /nvme/openbmc $ . openbmc-env $ cd .. $ source ./setup mtjade $ bitbake obmc-phosphor-image
if system it mt.mitchell
$ export TEMPLATECONF=meta-ampere/meta-mitchell/conf/templates/default/ $ export TMPDIR=/nvme/temp $ export LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8 $ cd /nvme/openbmc $ . openbmc-env $ cd .. $ source ./setup mtmitchell-dcscm $ bitbake obmc-phosphor-image
When compile, there is an openocd compile error, it cannot access to original website probably caused by the website was down. Temperory solutoin is to remove the package.
modify file meta-ampere/meta-common/recipes-ac01/packagegroups/packagegroup-ampere-apps.bb, find openocd and delete it, down.
When finish compile, the binary will locate on tmp/deploy/images/mtjade/, absoult path is /nvme/openbmc/build/mtjade/tmp/deploy/images/mtjade/
ex: (only list partical files)
obmc-phosphor-image-mtjade-20220616040212.rootfs.manifest obmc-phosphor-image-mtjade-20220616040212.rootfs.squashfs-xz obmc-phosphor-image-mtjade-20220616040212.static.mtd obmc-phosphor-image-mtjade-20220616040212.static.mtd.all.tar obmc-phosphor-image-mtjade-20220616040212.static.mtd.tar obmc-phosphor-image-mtjade-20220616040212.testdata.json obmc-phosphor-image-mtjade.jffs2 obmc-phosphor-initramfs-mtjade-20220616004506.rootfs.cpio.xz obmc-phosphor-initramfs-mtjade-20220616004506.rootfs.manifest obmc-phosphor-initramfs-mtjade-20220616004506.testdata.json
obmc-phosphor-image-mtjade-20220616040212.static.mtd.tar is firmware file, it contain both obmc-phosphor-image-mtjade-20220616040212.static.mtd and obmc-phosphor-image-mtjade-20220616040212.rootfs.manifest files, and can be used for next step : firmware update.
Upgrade Firmware
*Notice: Update flash will take your own risk, especially physical damage your hardware..
If Mt. Jade is using AMI bios, suggest to use flash burner to update the OpenBMC firmware.
What I am using is GZU EZP XPro , it’s very cheap, only needs around US$30.- (please also purchase the SPI flash socket).
This step need to un-plug BMC flash from Mt. Jade motherboard, please remeber the flash pin 1 location, it needs to follow the original position and put it back to socket. If you miss you will broken it.
Update OpenBMC firmware
ref. OpenBMC Code Update
Update via URL
Suppose that it already has OpenBMC firmware, it can use software to upgrade firmware ,
first step is to get web token, then use this token on next step to upgrade firmware.
Following is a simple script to upgrade flash, it can be integrated into your script.
export BMC_IP=192.168.1.190
export FWFILE=obmc-phosphor-image-mtjade-20220616040212.static.mtd.tar
export token=`curl -k -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST https://${BMC_IP}/login -d '{"username" : "root", "password" : "0penBmc"}' | grep token | awk '{print $2;}' | tr -d '"'`
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 84 100 37 100 47 116 147 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 264
curl -k -H "X-Auth-Token: $token" \
-H "Content-Type: application/octet-stream" \
-X POST -T ${FWFILE} \
https://${BMC_IP}/redfish/v1/UpdateService
{
"@odata.id": "/redfish/v1/TaskService/Tasks/1",
"@odata.type": "#Task.v1_4_3.Task",
"Id": "1",
"TaskState": "Running",
"TaskStatus": "OK"
}
If conosle doesn’t not update and reboot, please use console login the OpenBMC and run “reboot” manually.
It will show message like below on OpenBMC console.
Updating kernel... Erasing block: 69/69 (100%) Writing kb: 4397/4397 (100%) Verifying kb: 4397/4397 (100%) Updating rofs... Erasing block: 366/366 (100%) Writing kb: 11580/23376 (49%)
Update via SSH
Just update firmware (ex: obmc-phosphor-image-mtjade-20220616040212.static.mtd.tar) to BMC’s directory /tmp/images , it will shows a hash number like /tmp/images/d6718c8f, then run the following command
busctl set-property xyz.openbmc_project.Software.BMC.Updater \
/xyz/openbmc_project/software/d6718c8f \
xyz.openbmc_project.Software.Activation RequestedActivation s \
xyz.openbmc_project.Software.Activation.RequestedActivations.Active
Update UEFI firmware
Upgrade UEFI firmware
it needs to pack the UEFI image first , and it need to create MANIFEST file, looks like this
VER_purpose=xyz.openbmc_project.Software.Version.VersionPurpose.Host version=jade_tianocore_atf_2.06.100 KeyType=OpenBMC HashType=RSA-SHA256 MachineName=mtjade
make image file and MINIFEST file into the same file
$ tar -cvf jade_tianocore_atf_2.06.100.tar jade_tianocore_atf_2.06.100.img MANIFEST
Run command below to upgrade UEFI firmware
export BMC_IP=192.168.1.190
export FWFILE=jade_tianocore_atf_2.06.100.tar
export token=`curl -k -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X POST https://${BMC_IP}/login -d '{"username" : "root", "password" : "0penBmc"}' | grep token | awk '{print $2;}' | tr -d '"'`
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 84 100 37 100 47 116 147 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 264
curl -k -H "X-Auth-Token: $token" \
-H "Content-Type: application/octet-stream" \
-X POST -T ${FWFILE} \
https://${BMC_IP}/redfish/v1/UpdateService
Like OpenBMC, if it doesn’t update, just reboot to update it.
if stiall not work, try to upgrade it manually, yes, when I wrote this article, update via redfish doesn’t work, so, just copy it from github.
# on HOST $ scp jade_tianocore_atf_2.06.100.tar root@192.168.1.190:/tmp # on Target $ cd /tmp/images $ mkdir fw $ cd fw $ tar xvf /tmp/jade_tianocore_atf_2.06.100.tar $ firmware_update.sh /tmp/images/fw --- Current Chassis State: On --- Turning the Chassis off --- Switch the host SPI bus to BMC. Run update Primary Host SPI-NOR --- Bind the ASpeed SMC driver --- Locking power control --- Flashing firmware to @/dev/mtd13 Erasing block: 157/157 (100%) Writing kb: 9985/9985 (100%) Verifying kb: 9985/9985 (100%) --- Unlocking power control --- Switch back to the primary Host SPI-NOR. Turn on the Host
Update SCP firmware
It needs to use sftp to transfer SCP firmware to target.
Following is example to upgrade SCP firmware.
On host $ scp altra_scp_signed_2.06.20220426.slim root@192.168.1.190:/tmp On OpenBMC side $ ampere_firmware_upgrade.sh smpmpro /tmp/altra_scp_signed_2.06.20220426.slim
After upgrade BIOS and SCP, if got any problem, suggest to reset bmc
$ ipmitool -U root -P 0penBmc -I lanplus -C 17 -H 192.168.2.18 mc reset cold
Serial Console
it can use command to get system CPU console.
# CPU console $ ssh root@192.168.190 -p 2200
Reference
Ampere OpenBMC github
EDK2 Ampere Tool
Ampere EDK2
Ampere Computing Github
Error Message
Error: TEMPLATECONF value (which is /nvme/openbmc/meta-ampere/meta-mitchell) must point to meta-some-layer/conf/templates/template-name
Error message
Initializing OE build env
Error: TEMPLATECONF value (which is /nvme/openbmc/meta-ampere/meta-mitchell) must point to meta-some-layer/conf/templates/template-name
This is because followed the old configuration, it needs to point to right folder like
export TEMPLATECONF=meta-ampere/meta-jade/conf/templates/default/ . openbmc-env
.




Andrew Ernest
Thank you for this detailed post. I picked up a few Mt Jade servers on eBay and am thinking to upgrade the BMC. I added a second CPU to the open socket, but it seems hard-coded as disabled in the BIOS, so I’m hoping an updated BMC will open up the ability to re-enable the socket. Any insights you might have would be greatly appreciated.